Whai Is Snapshot Vmware
Table of Contents.What is VMware Snapshot?VMware Snapshot preserves the state and data of a virtual machine at a specific point in time.Snapshot state includes the virtual machine’s power state (ex, powered-on, powered-off, suspended) and the data includes all of the files (disks, memory, and other devices, such as virtual network interface cards.) that make up the virtual machine.Snapshots extremely simplify the Virtual Machine OS management and maintenance tasks by preserving the current state of the virtual machine. Snapshot without Virtual Machine’s Memory option:Snapshot taken without memory option will not capture the live state of the virtual machine. Snapshot creates crash consistent disks, which you can be used to restore the virtual machine to the state prior to the snapshot but it won’t revert the VM into same power state as it during snapshot creation.Virtual Machine can be either in Powered on or Powered off state to take VM snapshot without memory option.Let’s say I have taken a snapshot when the virtual machine is powered on and before the patch upgrade. After I revert back to the snapshot taken without memory, the Virtual machine will be restored to the same data and state but power state of the virtual machine won’t be Powered on.
It will be powered off. You need to manually power on the VM after reverting the snapshot.VM Snapshot with Quiesce Guest File SystemIf you select the option “ Quiesce guest file system” when taking snapshot, flag is 1 or true, It quiesce the file system in the virtual machine.
Quiescing a file system is a process of bringing the on-disk data of a physical or virtual computer into a state suitable for backups. This process might include such operations as flushing dirty buffers from the operating system’s in-memory cache to disk, or other higher-level application-specific tasks.The virtual machine needs to be “powered on” State to take a snapshot with the quiesce file system option and also it requires to be installed on the Guest OS to quiesce the file system in the virtual machine.Note: Quiescing indicates pausing or altering the state of running processes on a computer, particularly those that might modify information stored on disk during a backup, to guarantee a consistent and usable backup. Quiescing is not necessary for memory snapshots; it is used primarily for backups.How does VMware Snapshot work?. When you initiate the request to create, delete or revert snapshot operation via client (Web Client, vSphere Client or Power CLI), Request will be sent from the client to Server using VMware API. Snapshot create, delete or revert request will be forwarded to the ESXi host where that particular virtual machine is running. This process will happen only when initiating the snapshot create, delete or revert request from. Vampire the masquerade bloodlines weapons. Let’s see the step by step demo to understand the Revert to Snapshot option.

The problem here is you can’t tell which VM has the snapshot, just that the snapshot exists. Turns out there is a VM property in Get-Snapshot, so it was just a matter of using Select to get that information. But by now, you must know I can never let something sit at just that.
I have created a Folder called “File 1” created on the desktop of the virtual machine. File 1 folder is 6.48 GB of Size before taking the snapshot.I am creating the snapshot called “Snap1”Specify the Snapshot name and description. I am taking the memory snapshot of the virtual machine to revert to live state of the virtual machine.Once the snapshot “Snap1” is created for the virtual machine, I am deleting the folder “File 1” from the desktop.I have deleted the folder “File 1”. Let’s revert the virtual machine to the snapshot “Snap1”. To revert to the snapshot “Snap1”, Select the snapshot “Snap1” and Click on “Revert To” to revert to the snapshot.Click on “Yes” to confirm to revert to snapshot “Snap1”Revert to snapshot is completed successfully.Once Revert to the snapshot “Snap1” is completed, Virtual machine “winsvr” is reverted to the state when you to took the snapshot.
Since I have created a folder “File 1” prior to creating a snapshot. File 1 reappeared on the desktop.When you revert a virtual machine with snapshot, the current snapshot (delta disk) will be removed and a new one will be created linking to the parent disk. For Example, I have only one snapshot “Snap1” and it has its delta file called “winsvr-000001-delta.vmdk”. After reverting the virtual machine to snapshot “Snap1”, winsvr-000001-delta.vmdk got deleted and new delta file called “winsvr-000002-delta.vmdk is created.Reverting VMware Snapshot One level above the Current SnapshotLet’s take a look at the Scenario of Revert to the snapshot One level above the current snapshot. For Example, You have a virtual machine with 2 Snapshots “Snap1” & “Snap2”. Snap2 is the current snapshot.
This scenario talks about reverting your virtual machine to Snapshot 1 “Snap1” instead of recent snapshot “Snap2”.Let’s revert to the Snapshot 1 “Snap1”. Select the snapshot “Snap1” and Click on “Go To” to revert the virtual machine to Snapshot 1.When reverting to the Snapshot 1 “Snap1”, All the files, folders and changes made after the Snapshot 1 will be lost. I don’t see any of the folders created after Snapshot 1.An interesting fact is There is no longer “Winsvr-000002-delta.vmdk” delta file present and New delta file called “Winsvr-000003-delta.vmdk” is created.Virtual Machine VMDK also mapped with the newly created disk “winsvr-000003.vmdk”All the active writes to the virtual machine are passed to the newly created virtual machine. You can notice the new delta file 000003-delta.vmdk.
The new delta file is growing when new writes are coming. It has grown from 49 MB to 2.8 GB.
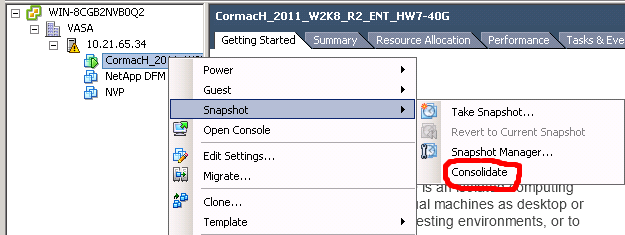
Snapshot ConsolidationSnapshot Consolidation is intended to resolve the problems that might occur with the snapshots. Snapshot consolidation is a method to commit a chain of snapshots to base disks when Snapshot manager shows no snapshots exist but the delta files are present in the virtual machine directory on the datatsore.Snapshot consolidation is a way to clean unneeded snapshot delta files from a datastore. Left out delta files may continue to grow until the virtual machine runs out of datastore space.With snapshot consolidation, vCenter Server displays a warning when the descriptor and the snapshot files do not match. After the warning is displayed, the user can use vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client to commit the snapshots.To Perform consolidation, Click on Snapshot - ConsolidateClick on “Yes” to confirm the consolidated operation.Limitations of VMware SnapshotKeeping snapshots for a longer duration than recommended can affect the virtual machine performance and also VM snapshot is not supported for some disk types and VM configured with bus sharing. Let’s understand what is the limitation of Virtual Machine Snapshots:.
VMware Snapshot is not supported for raw disks and RDM Physical mode disks. Snapshot is supported for RDM with virtual compatibility mode. VMware Snapshot does not support for independent disks. Virtual machines with independent disks must be powered off before you take a snapshot.

Esx Snapshot
VSphere Client Version: 4.0.0vCenter Version: 4.0.0TL:DR – Highlight your Cluster Storage Views Tab Reports button Check the snapshot space.You can’t. You can’t just get a nice map or an overview of every snapshot listed for every VM. VSphere just doesn’t have the capability to do that for you, no matter how convenient it would be for you. If you’re doing anything like our ideal environment, we backup our VMs at a vmdk level using snapshot technology through. It’s very reliable and really quick, especially if you’re using a SAN. Here’s how it works:. Backup Begins.
A snapshot (basically a full image copy of the vmdk file) is taken. VEEAM backs up the snapshot so the VM isn’t bogged down with anything other than IO or bandwidth traffic, depending on how your network is set up.
What Is Memory Snapshot In Vmware
When the backup completes, VEEAM deletes the snapshot. Backup EndsBut VEEAM has some rules. There cannot already be snapshots taken of the VM. If there are, it will create its own snapshot as well, but it will delete them all at the end of the job. And even though its reliable, sometimes a snapshot will hang for some reason and not get backed up. Needless to say, there needs to be a way for administrators to view what snapshots have been taken in order to make sure everything runs smoothly. Granted, this method doesn’t give you the chance to see how many snapshots are taken, but you should be familiar enough with your environment to know based on the sizes of the snapshots:Highlight your Cluster Storage Views Tab Reports button Check the snapshot spaceIt should give you a good idea of where you’re at, without all the clicking.
Comments are closed.